Developing pulsed-irradiation micro-CT for detailed in vivo and ex vivo three-dimensional biological tissue imaging

-
- Principal Investigator
Assistant Professor / Takayuki OKAMOTO
- Affiliation
Center for Frontier Medical Engineering, Chiba University
Researchmap
ORCID ID
- Principal Investigator
Micro X-ray computed tomography (micro-CT) is an imaging modality that offers significantly higher spatial resolution than medical CT scanners. It allows non-destructive observation of the three-dimensional (3D) internal structure of tiny objects (from a few millimeters to a few centimeters) and plays an important role in inspecting industrial products and complex electronic components. In recent years, micro-CT has also been widely used for pathological examinations and in vivo imaging in preclinical research to analyze the 3D characteristics of biological tissues.
In pathological examinations of solid biological tissues, the traditional method involves observing thin-sectioned specimens under a microscope. However, due to the complexity of preparing these thin sections, the sampling intervals tend to be coarse, making detailed observation of the 3D structure difficult. Micro-CT has the potential to overcome these challenges by providing detailed 3D structural information in a single scan.
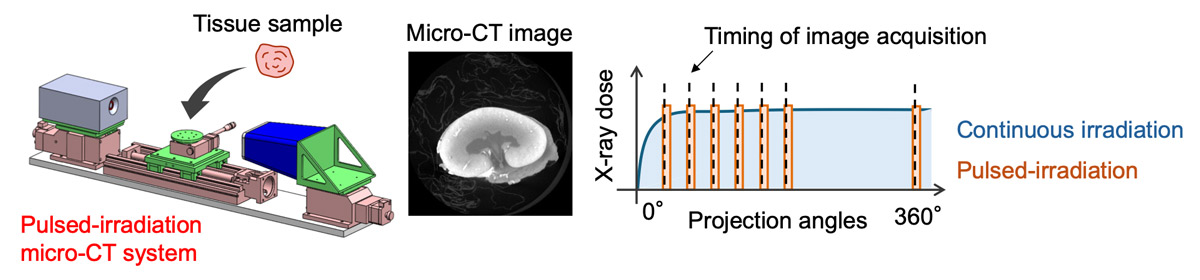
Attempts to introduce micro-CT into pathological examinations have been reported domestically and internationally; however, many of these studies use large, powerful, and expensive micro-CT systems. Available X-ray sources generally require continuous X-ray emission during imaging, which requires large power and cooling systems. In addition, prolonged X-ray exposure is required to improve the quality of micro-CT images, raising concerns about potential tissue damage.
This study focuses on X-ray sources that enable pulsed irradiation for short durations. I aim to design and develop a compact micro-CT system by reducing power consumption and miniaturizing power and cooling systems. Using the image reconstruction technology I have developed for high-speed imaging, I will work to develop a pulsed-irradiation micro-CT that allows for energy-efficient, space-saving, low-radiation exposure, and rapid imaging from both hardware and software perspectives.