Elucidation of molecular pathology of proteostasis in body fluids

-
- Principal Investigator
Professor / Eisuke ITAKURA
- Affiliation
Graduate School of Science, CHIBA University
Researchmap
ORCID ID
- Principal Investigator
Protein quality control systems that remove aberrant proteins are crucial in living organisms because of their important functions. Within cells, there are intracellular protein degradation pathways such as autophagy and the proteasome that maintain proteostasis*. These pathways ensure the proper degradation of intracellular proteins.
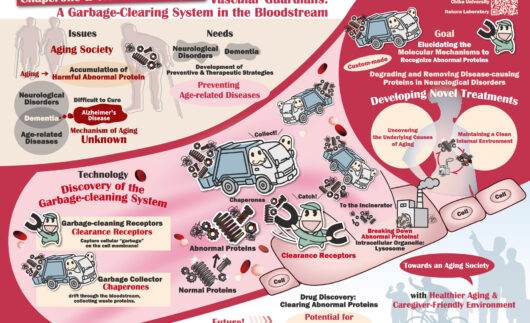
In the bodies of mammals, proteins are abundant not only inside cells but also in the extracellular environment, such as in blood and interstitial fluid, where they perform various functions. However, the pathway for degrading these aberrant extracellular proteins has not been well-understood.
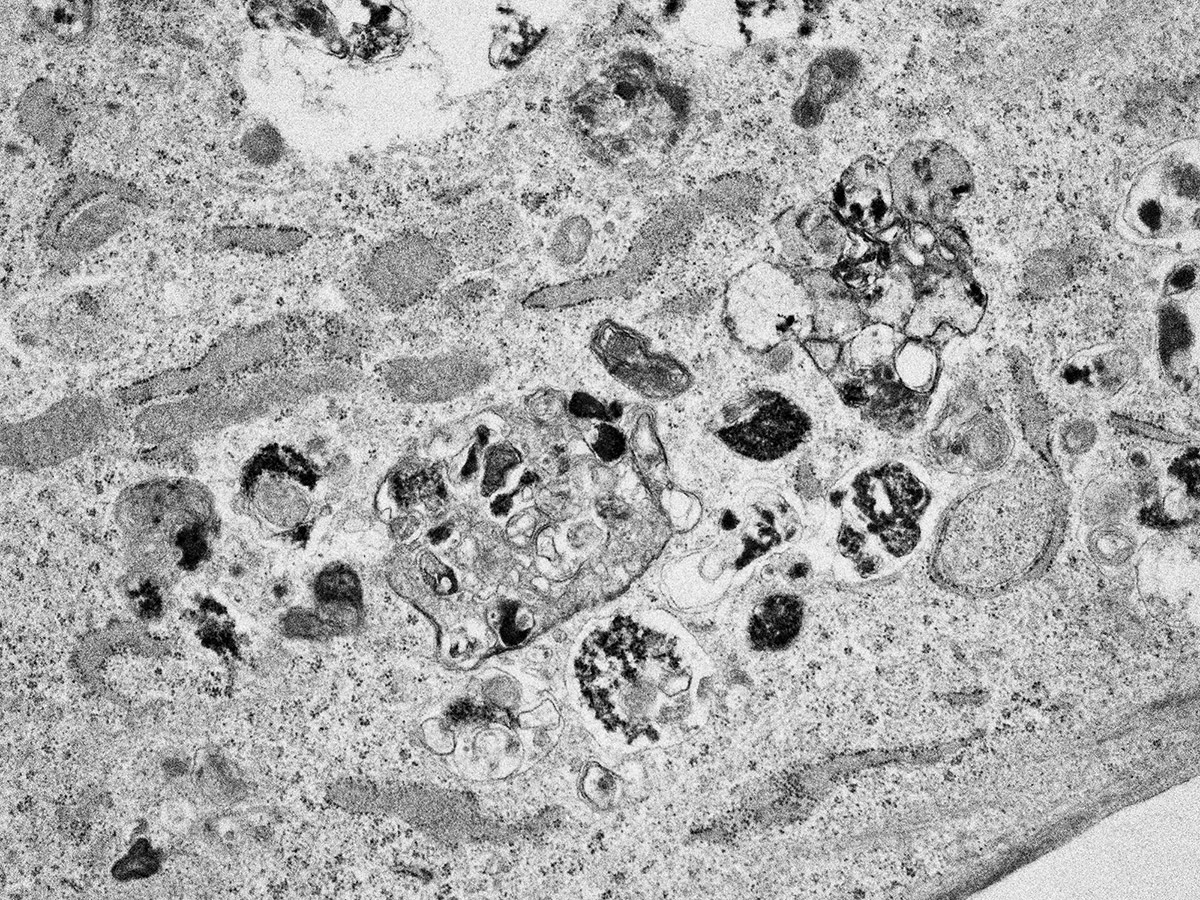
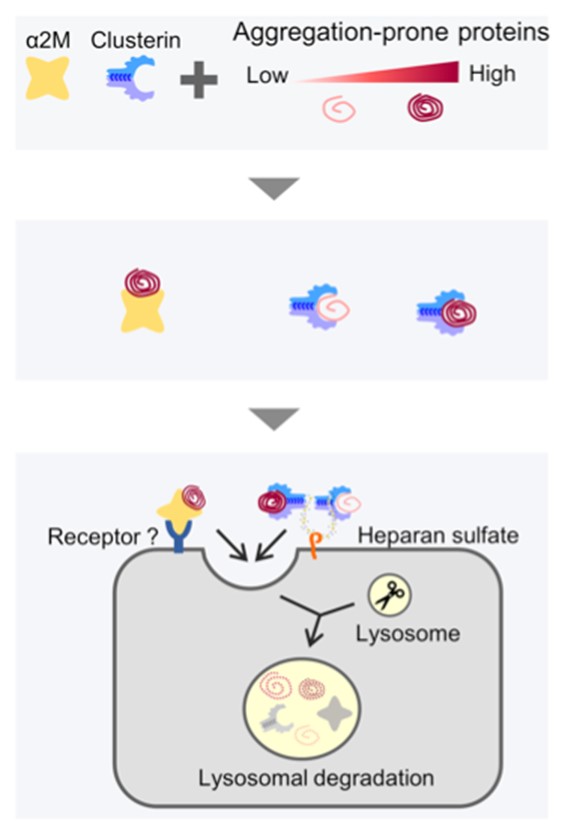
Recently, our team discovered a pathway that selectively degrades aberrant extracellular proteins. This pathway involves a protein called "extracellular chaperone" that selectively recognizes aberrant proteins, including amyloid beta, which is implicated in Alzheimer's disease, and directs them to lysosomal degradation inside cells. However, the mechanism and physiological importance of this pathway are still unknown.
In this research, we aim to identify novel extracellular chaperones involved in the degradation of disease-causing proteins in the blood and to analyze the selective substrate recognition, internalization, and degradation mechanism inside cells, as well as the physiological functions of chaperones. Using the advantages of the previously discovered extracellular protein degradation system, we will accelerate research on extracellular denatured protein degradation pathways in mammalian cells and mice.
This research will open up a new study field for proteostasis in body fluids to contribute to understanding the molecular mechanisms of protein accumulation diseases. Furthermore, the research aims to develop new treatment methods utilizing extracellular chaperones.
*Proteostasis refers to the state in which all proteins work together to achieve optimal efficiency and balance in the cell. If the proteostasis network is in equilibrium, the cell can be considered "healthy."