
-
Michiyo SATO(OKAMOTO)
Researchmap
Assistant Professor (Research fellowship-RPD)Institute for Advanced Academic Research / Medical Mycology Research Center
Keywords
Pathogen, Opportunistic infection, Sterol uptake, Intracellular transport, Drug resistance
Professional Memberships
The Japanese Society for Medical Mycology, Yeast Genetics Society of Japan
Research Theme
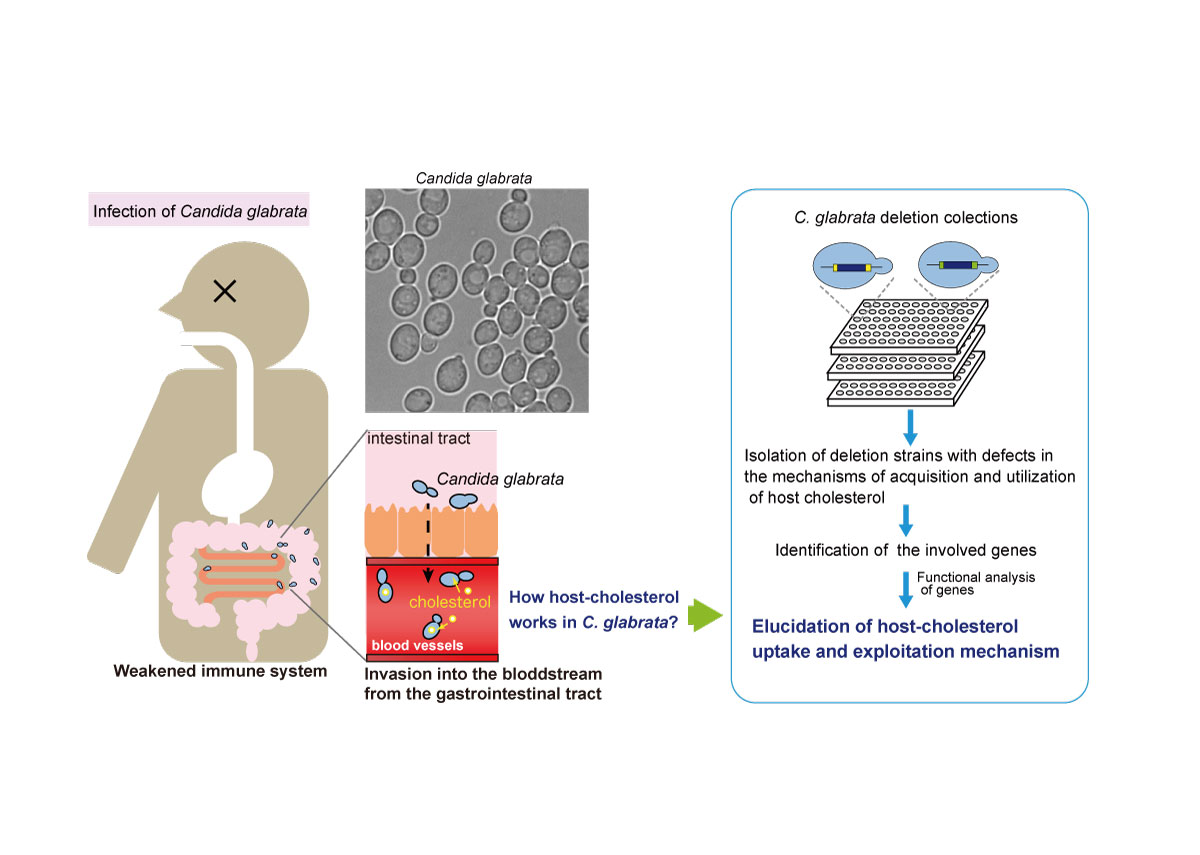
Mechanisms of host-cholesterol uptake and exploitation in pathogenic yeast
Abstract
Pathogenic fungal Candida species are yeasts that are endemic to the intestinal mucosa of humans and are not particularly problematic for healthy people. However, in people with severely weakened immune systems due to illness or aging, they can invade the bloodstream and cause serious bloodstream infections (with a fatality rate of 30% to 50%). Among these Candida species, I am focusing on Candida glabrata (C. glabrata), whose drug resistance has become a problem.
C. glabrata is phylogenetically very close to baker's yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. However, C. glabrata has an interesting mechanism for acquiring and utilizing cholesterol from the blood of the host (human). The details of this mechanism are unknown. At my laboratory, the collection consisting of gene-disrupted strains of C. glabrata has succeeded in elucidating the function of C. glabrata genes. In this study, by using this collection, I will elucidate how C. glabrata exploits the cholesterol acquired during host infection.
