-
Sougata DATTA
Researchmap
Research FellowChiba University Institute for Advanced Academic Research / Graduate School of Engineering
Keywords
Interlocked molecules, Topology, Catenan, Supramolecular polymers, Atomic force microscopy
Research Theme
Topological Supramolecular Polymers Open the Way to Mesoscale Polycatenanes

Abstract
Creating flexible one-dimensional structures using rigid materials is not an easy task, but it can be achieved by utilizing chain-like structures formed by the connection of rings.
Furthermore, these chain-like structures composed of ring-shaped molecules, known as catenanes, have the advantage of being repairable by simply replacing the damaged rings, even if the material is damaged.
Thus, catenanes are an essential research subject with the potential to impart dynamic properties to materials, improving their functionality and durability, and expanding their range of applications.
Jean-Pierre Sauvage, an emeritus professor at the University of Strasbourg in France, received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2016 for his discovery* of template-directed synthesis of catenanes.
Various catenane molecules, including polycatenanes, consisting of numerous interlocked rings, have been synthesized using this method.
Although polycatenanes are expected to have many applications as advanced functional materials, their synthesis has been complex and time-consuming.
Additionally, due to the large and flexible rings they are composed of, it was difficult to crystalize them, making the characterization of their properties has been extremely challenging.
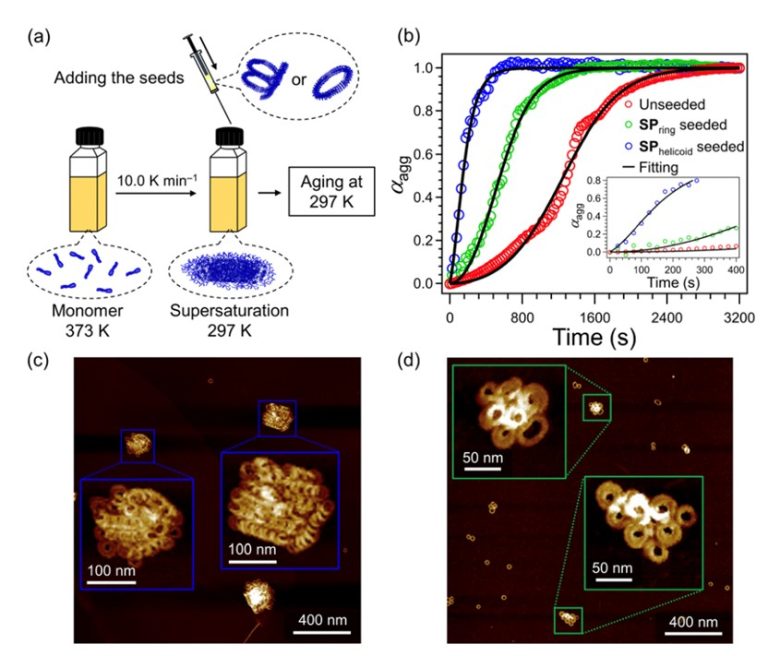
To address this challenge, we have created mesoscale polycatenanes that can be easily characterized using atomic force microscopy (AFM) (Figure).
These structures can be easily and simply created in one step through the self-assembly of numerous small molecules.
We aim to use these structures to create mesoscale machinery and devices in the future.
*One of the methods for synthesizing molecules, in which another molecule is synthesized along the three-dimensional shape of a molecule called a template. This method has made it possible to synthesize molecules with complex structures that were previously difficult to synthesize using conventional synthesis methods.