-
Akira SUTO
Researchmap
Associate ProfessorChiba University Institute for Advanced Academic Research / Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Graduate School of Medicine
Keywords
IL-21, Th17 cells, Treg cells, γδT17 cells, c-Maf, Sox5, Sox12, IL-6, TGF-β, Soluble IL-21 receptor, Intracellular cytokine staining methods
Professional Memberships
The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine, Japan College of Rheumatology, Japanese Society of Allergology, Japanese Society for Immunology
Research Theme
Elucidation of the Mechanisms of T cell Differentiation and Maintenance Involved in the Development of Autoimmune Diseases
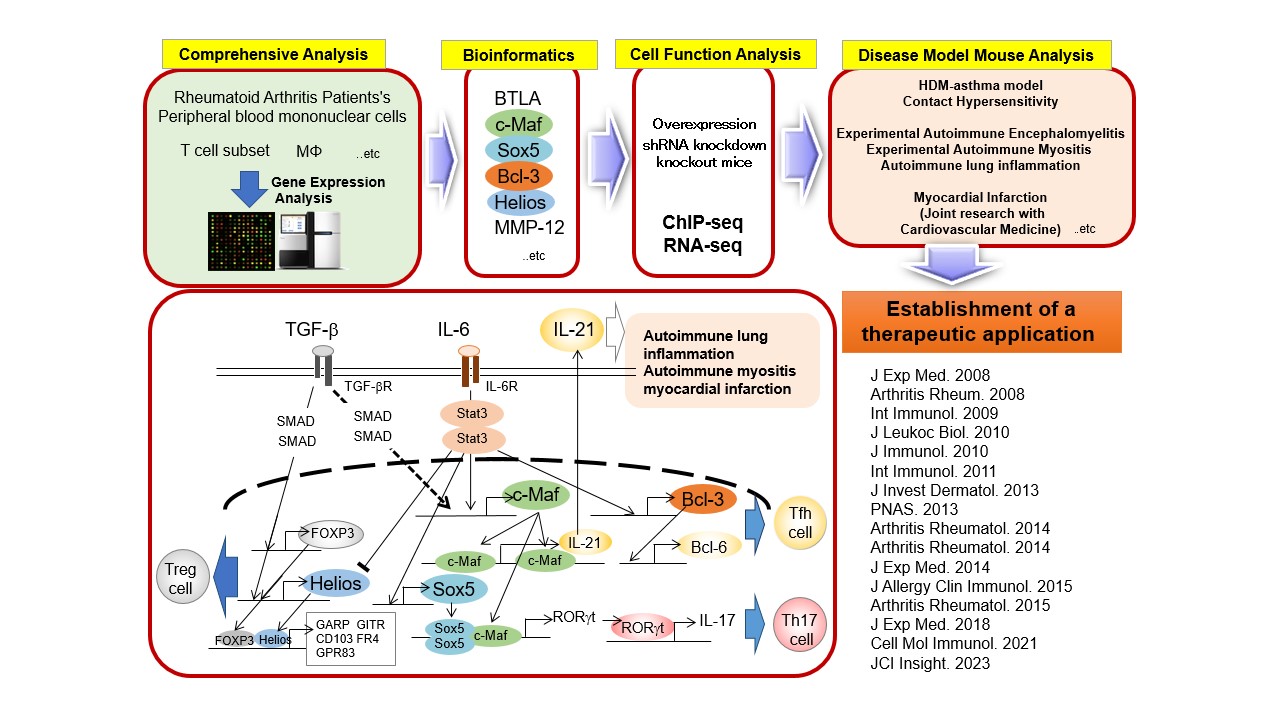
Abstract
1. Role of IL-21 in autoimmune disease onset
IL-21 is an autocrine growth factor produced by Th17 cells and T follicular helper cells, with an essential role in autoimmune diseases. We have demonstrated that IL-21 is involved in diabetes onset in NOD mice, autoimmune lung inflammation in Foxp3 mutant scurfy mice, and experimental autoimmune myositis. We also found that: (1) the transcription factor c-Maf induces the differentiation of IL-21-producing helper T cells; (2) IL-21 induces the proliferation of Vγ4+IL-17-producing γδT cells.
2. Role of Sox family molecules in helper T cell differentiation.
We have clarified that: (1) the transcription factors Sox5 and c-Maf are involved in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inducing RORγt, a key transcription factor in Th17 cells; (2) Sox12 is involved in the differentiation of peripherally induced regulatory T cells and suppresses the development of inflammatory bowel disease models.

